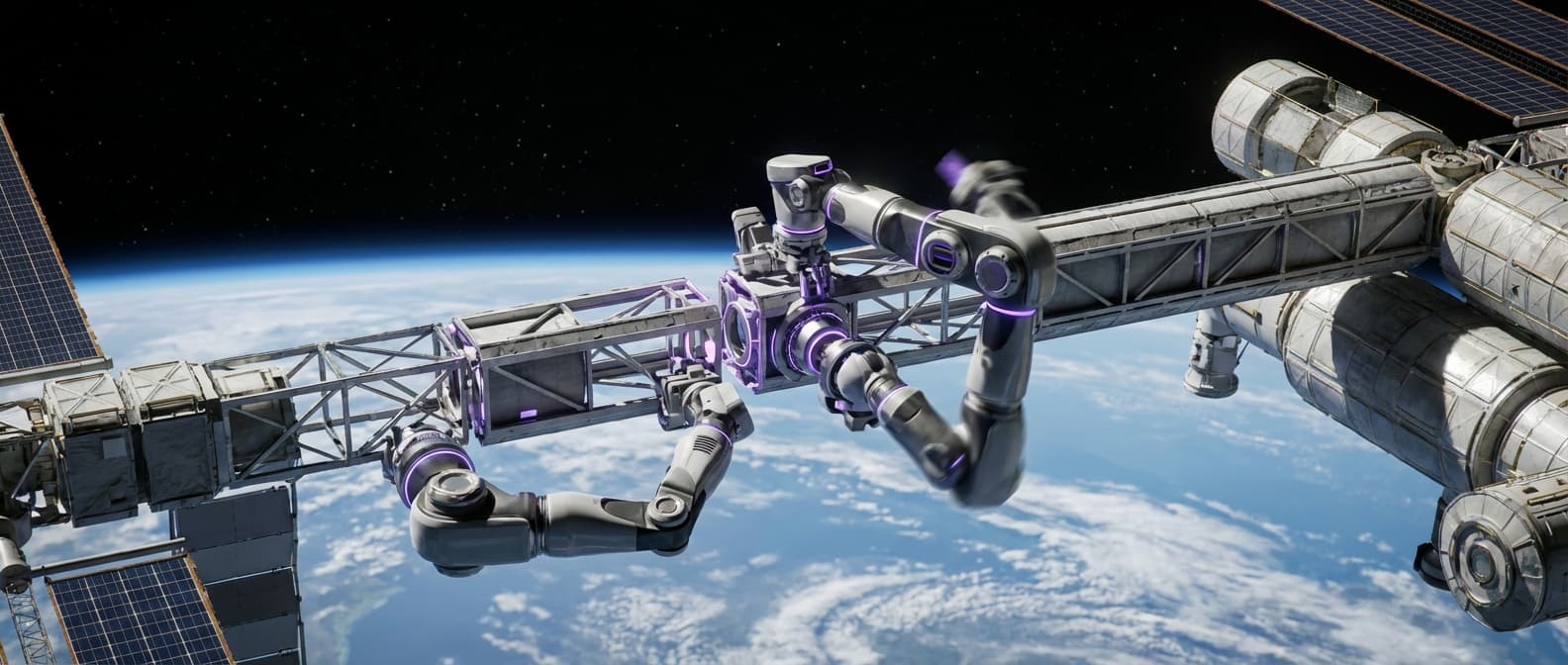
On-orbit manufacturing and assembly uses robotic systems, including free-flying robots and additive manufacturing modules, to construct large structures directly in space. These systems can assemble massive antennas, telescopes, solar arrays, and other structures that are too large to fit in rocket fairings, taking advantage of microgravity conditions that enable construction techniques impossible on Earth.
This innovation addresses fundamental limitations of space infrastructure, where the size of structures is constrained by what can fit inside rocket fairings. By manufacturing and assembling in space, these systems enable the construction of structures orders of magnitude larger than what can be launched, opening possibilities for massive space telescopes, solar power stations, and other infrastructure. Companies and space agencies are developing these capabilities, with some demonstration missions already completed.
The technology is particularly significant for enabling next-generation space infrastructure that requires large scale, such as space-based solar power, massive telescopes for astronomy, and large-scale space stations. As launch costs decrease and manufacturing capabilities improve, on-orbit manufacturing could become a standard approach for building space infrastructure, fundamentally changing how we think about space construction and enabling capabilities that were previously impossible.