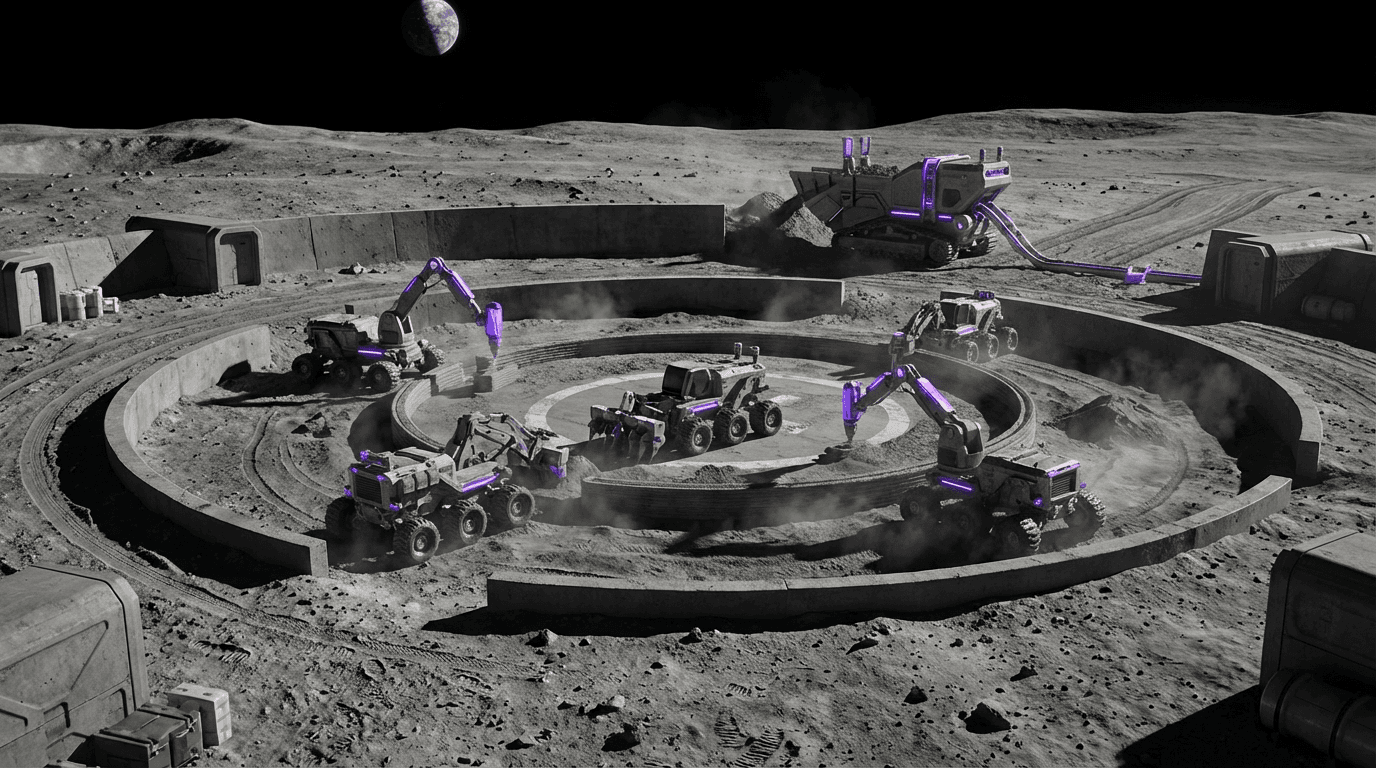
Lunar surface construction robotics encompasses teleoperated and autonomous robotic systems designed to perform construction tasks on the Moon using local materials (regolith), including grading terrain, sintering regolith (heating it to form solid structures), and assembling structures. These systems are key enablers for permanent lunar bases, capable of building radiation berms, landing pads, roads, and other infrastructure without requiring construction materials to be transported from Earth, dramatically reducing the cost and complexity of establishing lunar presence.
This innovation addresses the enormous cost and difficulty of transporting construction materials from Earth to the Moon, where every kilogram costs thousands of dollars to launch. By using local regolith as construction material, these systems enable the construction of large-scale infrastructure that would be impractical if all materials had to come from Earth. The technology is essential for establishing sustainable lunar bases and serves as a model for construction on Mars and other destinations. NASA and commercial companies are developing these capabilities for Artemis and future lunar operations.
The technology is critical for enabling long-term human presence on the Moon, where infrastructure like landing pads, radiation protection, and habitation structures are essential. As lunar exploration expands, construction robotics becomes essential infrastructure. However, the technology faces challenges including operating in the harsh lunar environment, ensuring construction quality, and developing reliable autonomous systems. The technology represents an important capability for space settlement, but requires significant development and demonstration. Success could enable sustainable lunar bases and serve as a stepping stone for Mars settlement, demonstrating how to build infrastructure in space using local materials.