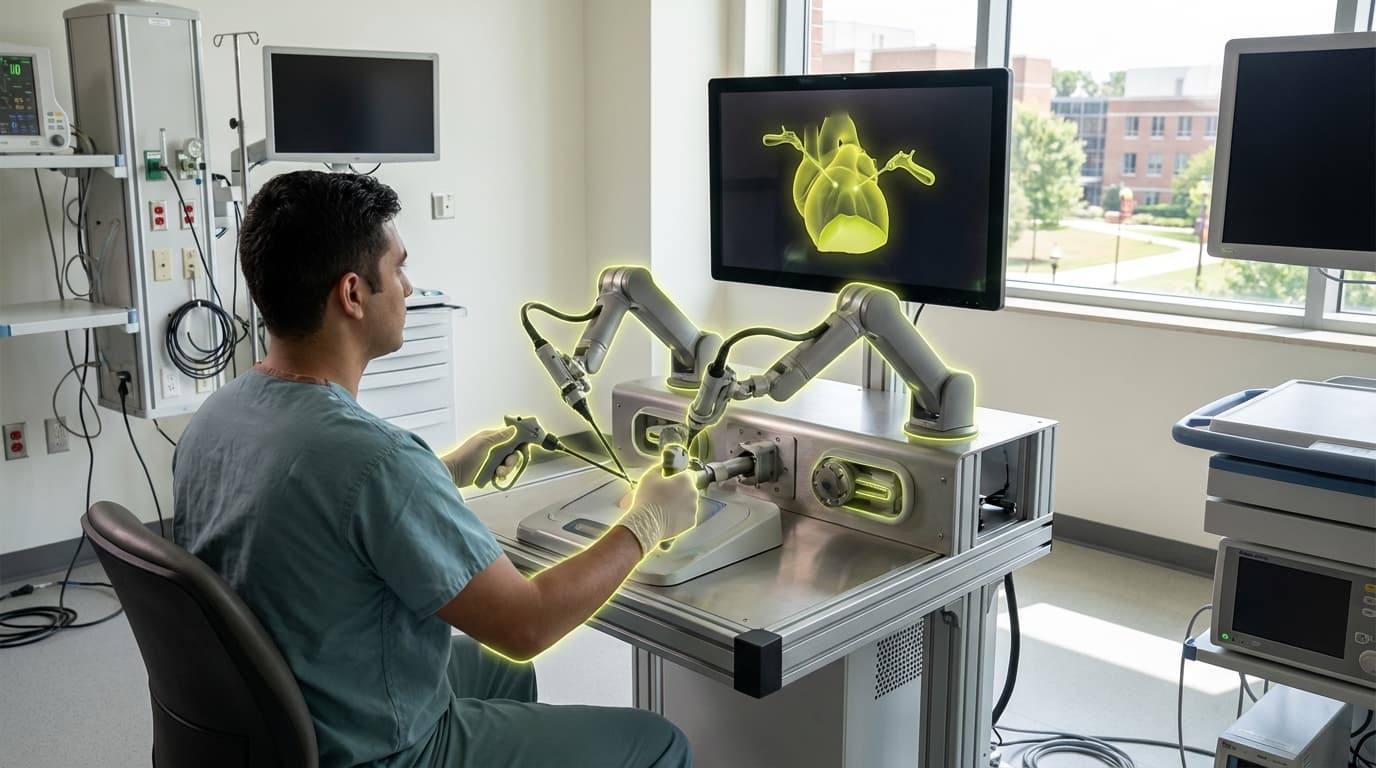
Haptic learning devices use force-feedback technology to provide tactile sensations—resistance, vibration, texture, and pressure—in digital learning environments, enabling learners to develop muscle memory and fine motor skills through virtual practice. These devices include haptic pens for handwriting practice, haptic gloves for surgical training, and specialized controllers for learning crafts, machining, or other hands-on skills. By simulating the physical sensations of real-world tasks, these devices enable safe, repeatable practice of skills that require precise motor control, allowing learners to develop proficiency before attempting real procedures or working with actual materials. Advanced systems can simulate different textures, resistances, and forces, providing realistic feedback that enhances skill development.
This innovation addresses the challenge of teaching hands-on skills safely and efficiently, where traditional methods may involve expensive materials, safety risks, or limited practice opportunities. By providing realistic haptic feedback in virtual environments, these devices enable extensive practice without material costs or safety concerns. Companies developing haptic technology for education and training include HaptX, various medical simulation companies, and educational technology providers exploring haptic applications.
The technology is particularly significant for skill-based learning in fields like medicine, crafts, and technical trades, where hands-on practice is essential but opportunities may be limited. As haptic technology improves and becomes more affordable, haptic learning devices could become standard tools for motor skill training. However, ensuring realistic feedback, managing costs, and demonstrating clear learning benefits remain challenges. The technology represents an important tool for skill-based learning, but requires continued development to achieve the realism and affordability needed for widespread adoption.