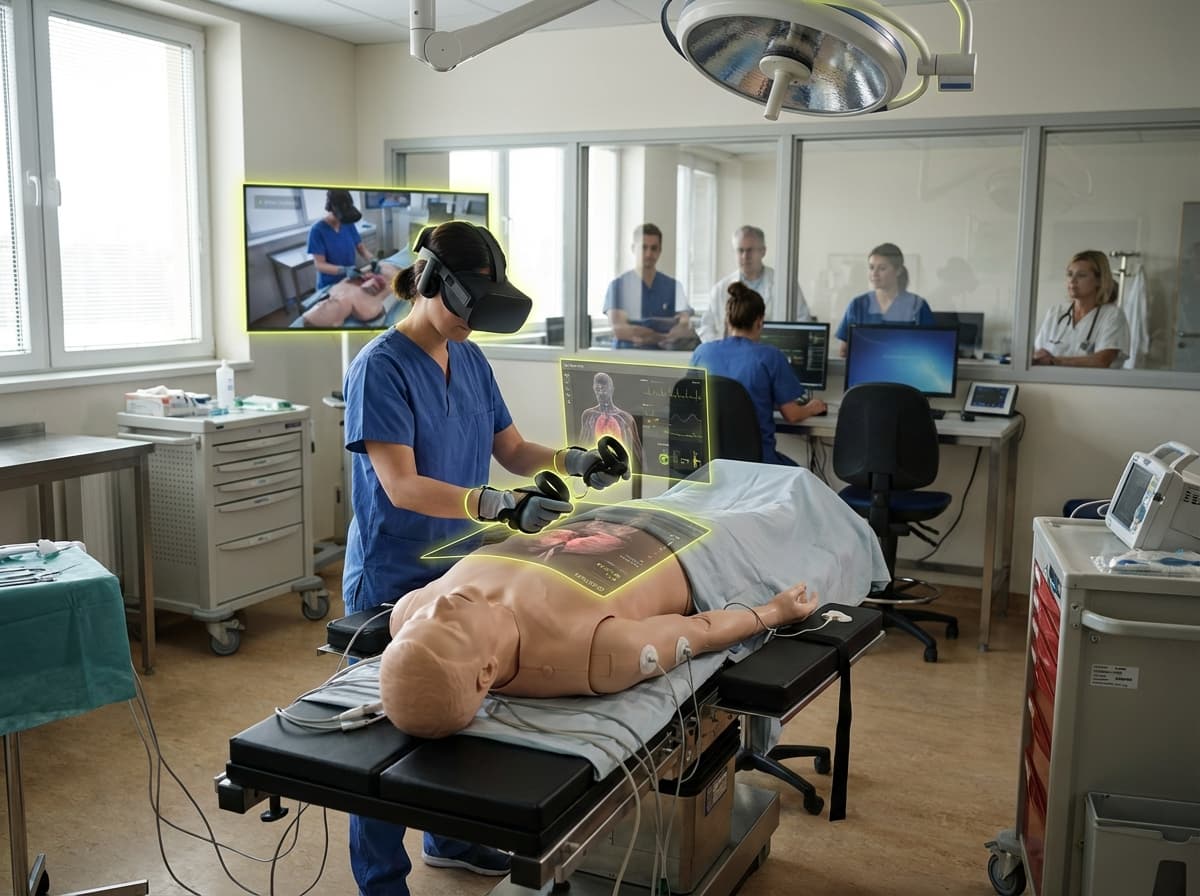
Simulation-Based Medical Training
Related Organizations
A world-leading provider of training, educational, and therapy products for emergency medical care.
A global leader in healthcare simulation solutions.

A world-leading provider of training, educational, and therapy products for emergency medical care.
A global leader in healthcare simulation solutions.
United Kingdom · Company
Delivers haptic VR flight simulators for surgery, allowing doctors to feel tissue resistance.
Designers and manufacturers of medical simulators for healthcare education.
A surgical training and assessment platform using VR to allow surgeons to practice procedures.
Delivers virtual reality medical simulation for training healthcare professionals.
A leader in 3D printing that also produces the Touch™ haptic devices (formerly Geomagic/Sensable) for medical and vocational training.
Simulation-based medical training uses high-fidelity mannequins, virtual reality (VR) environments, augmented reality (AR) overlays, and haptic feedback systems to provide realistic, safe practice environments for medical procedures, emergency response, and clinical skills before trainees work with real patients. These systems range from sophisticated mannequins that simulate physiological responses, breathing, and vital signs to VR environments that recreate surgical procedures, emergency scenarios, or complex clinical situations with realistic physics and haptic feedback. Advanced systems capture detailed performance metrics, provide real-time feedback, and enable repeated practice of procedures until proficiency is achieved, significantly improving patient safety by ensuring trainees are well-prepared before working with real patients.
This innovation addresses the critical need for safe, effective medical training, where learning on real patients carries unacceptable risks and where opportunities for practice may be limited. By providing realistic simulation environments, these systems enable extensive practice without risk to patients, improving both trainee competence and patient safety. Medical schools, hospitals, and training institutions worldwide use these systems, with simulation-based training becoming standard in medical education and continuing professional development.
The technology is particularly significant for medical education and patient safety, where simulation-based training has demonstrated clear benefits in improving clinical skills and reducing medical errors. As simulation technology improves and becomes more sophisticated, these systems could become even more effective training tools. However, ensuring simulation realism, managing costs, providing adequate feedback, and ensuring transfer of skills to real clinical contexts remain considerations. The technology represents a proven and essential approach to medical training, with clear benefits for both education and patient safety.