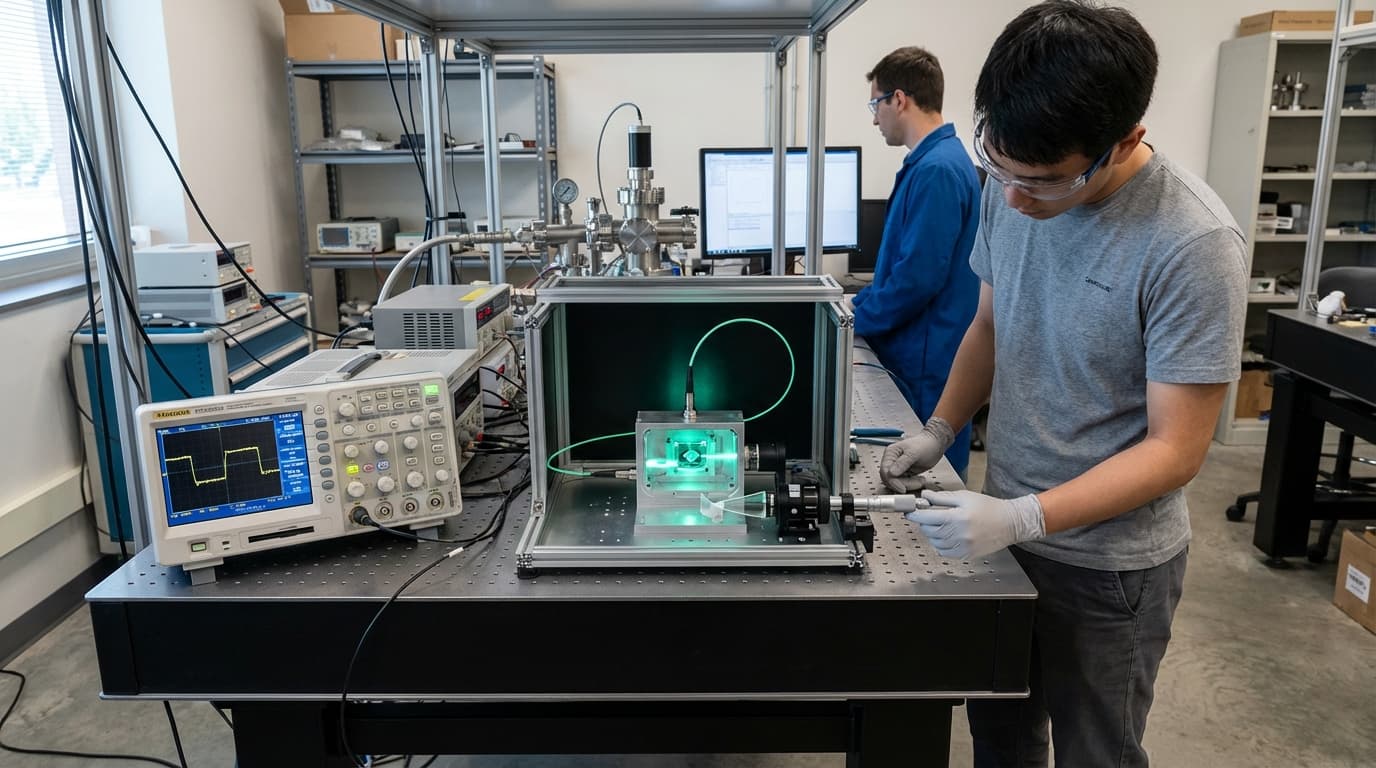
Nitrogen-vacancy (NV) diamond sensors are quantum sensing devices that use ensembles of NV centers (defects in diamond crystals) embedded in diamond chips, packaged into deployable magnetometers (devices that measure magnetic fields) and electrometers (devices that measure electric fields) for applications including biomedical imaging (detecting magnetic fields from brain activity), geoscience (exploring for minerals and oil), and navigation (precise magnetic field sensing). Operating at ambient conditions (room temperature and normal pressure), they unlock quantum-grade sensitivity (extreme precision enabled by quantum effects) without cryogenics (cooling systems), enabling mobile brain imaging systems and mineral exploration kits that can operate in practical environments, making quantum sensing accessible for real-world applications.
This innovation addresses the need for extremely precise sensing in practical environments, where most quantum sensors require extreme cooling. By operating at room temperature, NV diamond sensors enable practical quantum sensing. Companies and research institutions are developing these sensors for commercial applications.
The technology is particularly significant for enabling practical quantum sensing applications, where room-temperature operation makes quantum sensors usable in the field. As the technology improves, it could enable new sensing capabilities. However, ensuring sensitivity, managing diamond quality, and achieving commercial viability remain challenges. The technology represents an important evolution in quantum sensing, but requires continued development to achieve widespread use. Success could enable practical quantum sensing applications, but the technology must prove its value in real-world deployments. NV diamond sensors are already being used in some commercial applications.