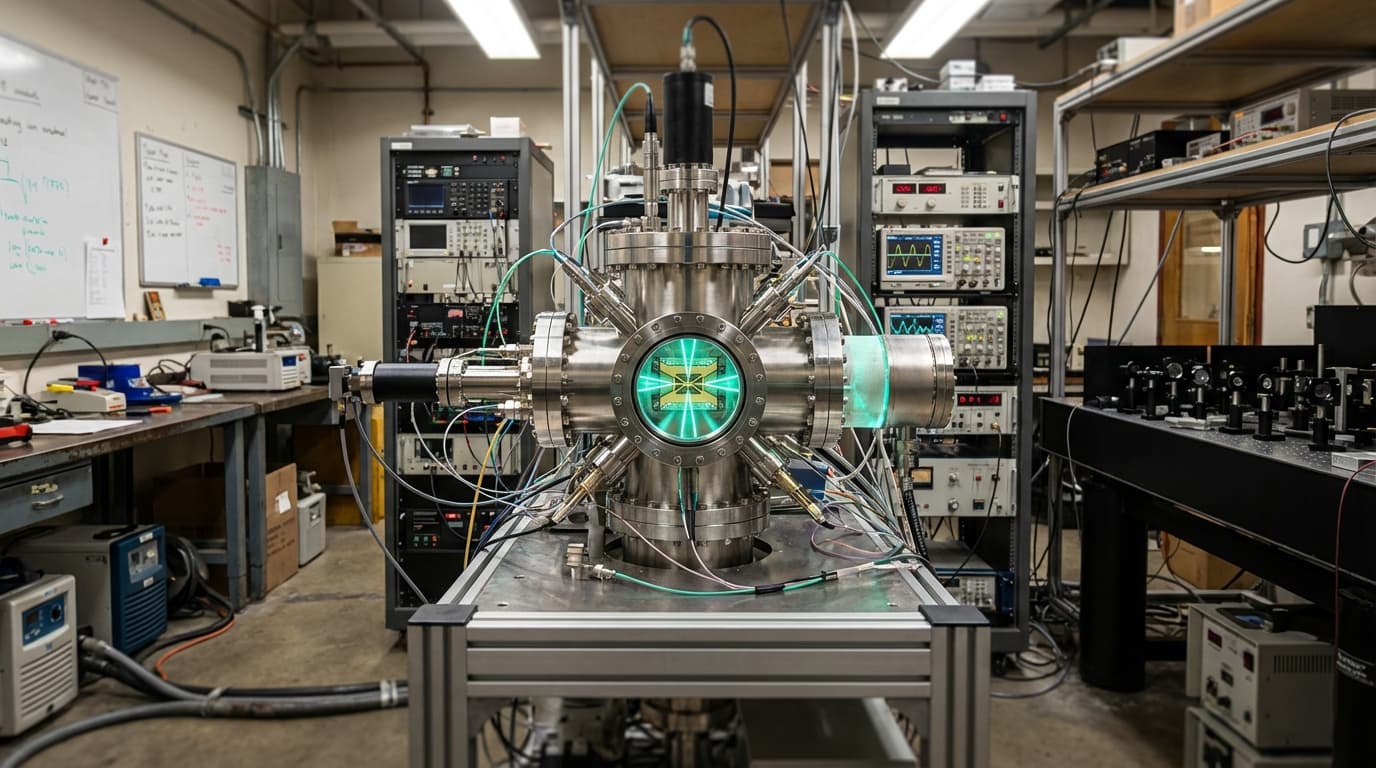
Trapped-ion quantum processors are quantum computing systems that use electromagnetic fields to suspend charged atomic particles (ions) in free space, creating qubits with some of the highest coherence times (how long quantum states remain stable) and gate fidelities (accuracy of quantum operations) available among current quantum computing approaches. These systems trap individual ions using electric and magnetic fields, allowing precise control and manipulation of quantum states, and recent advances in shuttling ions between zones on a chip (moving ions to different locations for different operations) are addressing the scalability challenges of this architecture, where connecting many ions together has been difficult, enabling larger trapped-ion quantum computers.
This innovation addresses the need for high-quality qubits in quantum computing, where trapped ions provide excellent performance. By improving scalability, these systems could enable larger quantum computers. Companies like IonQ, Quantinuum, and research institutions are developing these technologies.
The technology is particularly significant for quantum computing applications requiring high fidelity, where trapped ions provide excellent performance. As scalability improves, trapped-ion systems could become more practical. However, managing complexity, scaling to larger systems, and maintaining high performance remain challenges. The technology represents a mature approach to quantum computing, but requires continued development to achieve larger scale. Success could enable high-performance quantum computers, but the technology must continue to scale. Trapped-ion quantum computing is one of the most mature approaches, with several companies offering commercial systems.