
Develops high-performance edge computing computers for space.
A global edge-to-cloud company known for the 'Spaceborne Computer' experiments.
Provides commercial access to high-performance computing in orbit.
Provides on-board processing hardware and software for Earth observation satellites.
Through Copilot and the 'Recall' feature in Windows, Microsoft is integrating persistent memory and agentic capabilities directly into the operating system.
A major European satellite manufacturer leading the ASCEND feasibility study.
Operates LizzieSat satellites which offer edge computing as a service.
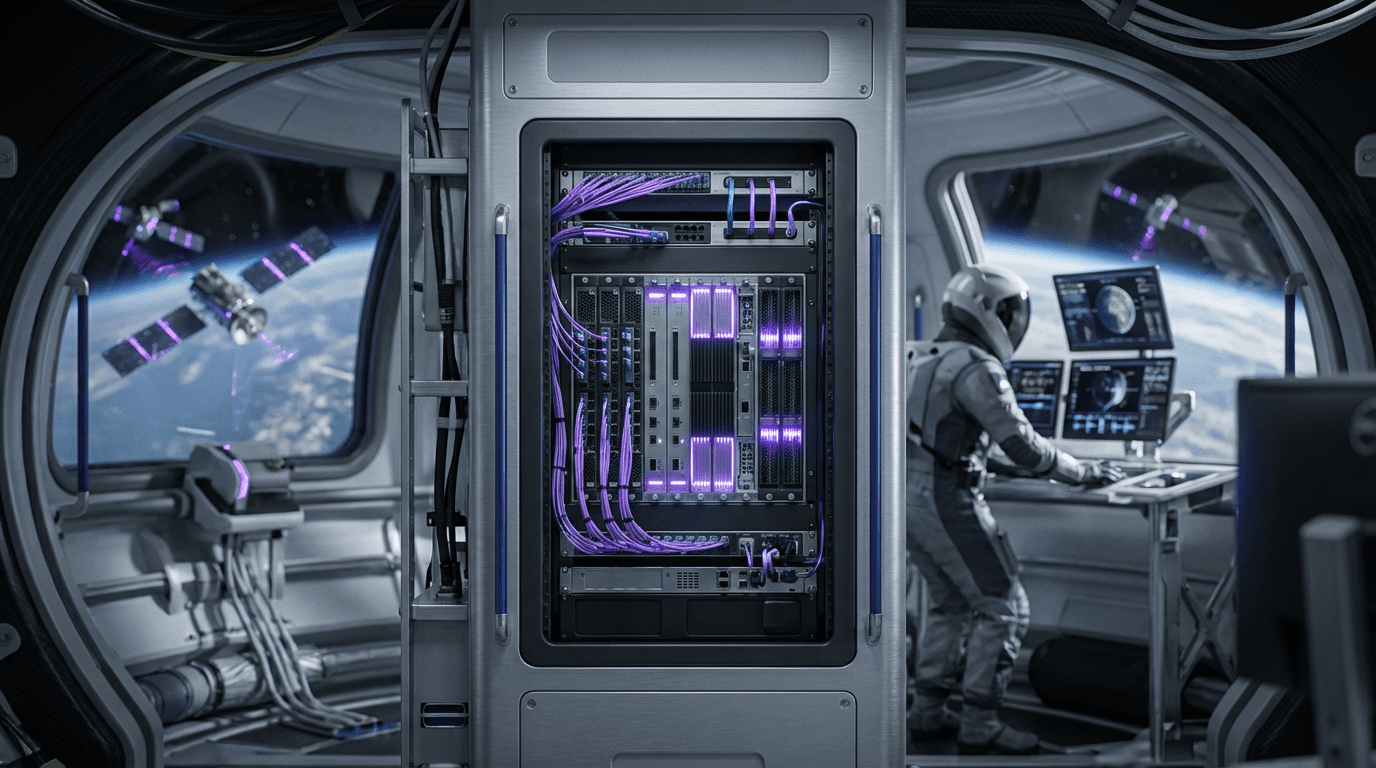
Orbital edge cloud computing deploys server-grade computing hardware directly on satellites to process massive Earth observation datasets in situ, rather than downlinking raw data for processing on Earth. By filtering, analyzing, and compressing data in orbit, these "cloud regions in space" dramatically reduce downlink bandwidth requirements and latency, enabling real-time or near-real-time insights from satellite data for applications including intelligence, disaster response, and environmental monitoring.
This innovation addresses the bandwidth bottleneck in Earth observation, where satellites collect far more data than can be efficiently downlinked. By processing data on-orbit, these systems can extract valuable information and send only the results, reducing communication requirements while enabling faster response times. The approach is similar to edge computing on Earth, but adapted for the unique constraints of space environments.
The technology is particularly valuable for applications requiring rapid response, such as disaster monitoring, security applications, and time-sensitive environmental monitoring. As satellite constellations grow and collect more data, on-orbit processing becomes essential for managing data volumes and providing timely insights. However, the technology faces challenges including radiation effects on computing hardware, power and thermal constraints, and the complexity of operating sophisticated computing systems in space. The technology represents an important evolution in satellite capabilities, enabling new applications and more efficient use of satellite data. As computing hardware becomes more space-hardened and efficient, orbital edge computing could become standard for Earth observation satellites.